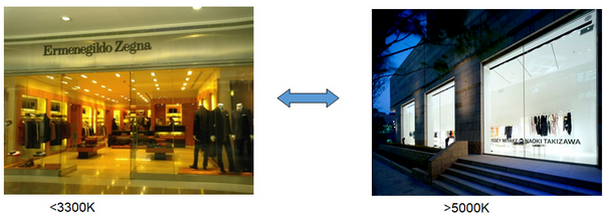
Color temperature
When a standard blackbody is heated (such as the tungsten wire in an incandescent lamp), the color of the blackbody begins to change gradually along the dark red - light red – orange – yellow – white - blue as the temperature increases. When the color of the light emitted by a light source is the same as that of the standard blackbody at a certain temperature, we call the absolute temperature of the blackbody at that time as the color temperature of the light source, represented by the absolute temperature: K.
(Common sense of color temperature) Table 1
| color temperature |
light color |
atmosphere effect |
|
>5000K |
cool (bluish white) |
cold and deserted feeling |
|
3300K-5000K |
middle (close to natural light) |
no obvious visual psychological effect |
|
<3300K |
warm (white with orange flowers) |
warm and sweet feeling |
(Color temperature perception) Table II
| color temperature |
perception |
light color |
feeling |
lighting effect |
|
2000-3000K |
0.5hours after sunrise |
Golden yellow- white with red |
warm |
dignified |
|
3000K-4500K |
2hours after sunrise |
white with yellow |
warm in the middle |
natural |
|
4500K-5600K |
4hours after sunrise |
white |
middle |
comfortable |
|
>5600K |
overcast |
white with blue |
cool in the middle |
brilliant |
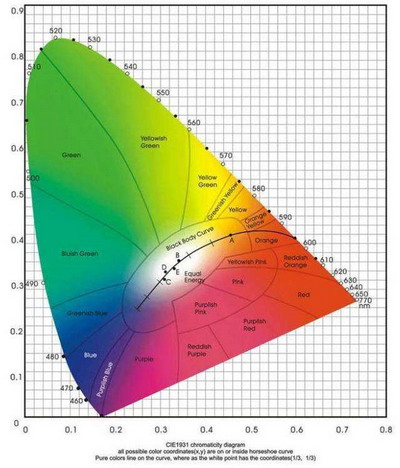
Color coordinates
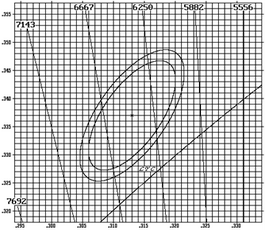
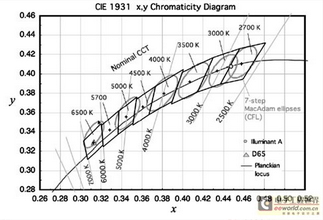
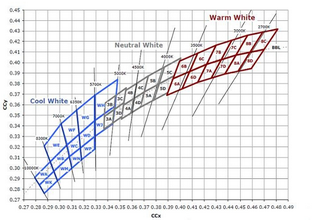
The coordinates on the blackbody track are called color temperature, and there are definite coordinates; the coordinates outside the blackbody trajectory (close to the blackbody trajectory) are called the correlated color temperature, also referred to as the color temperature. For example, for the color temperature of 6250k, the color coordinate x=0.3176 y=0.3275. Temperature, from low to high, all color temperature points form a (curve) line, which is called "blackbody color temperature trajectory".
However, the color temperature often referred to now is actually " correlated color temperature" (CCT); The "color temperature" is also used for the point (coordinate) that is not on the track but is not far away, and its color temperature value is the value of the point closest to the track. In this way, for the same color temperature, there are many points
outside the track, and the connecting lines of these points are called "isotherms"; That is, all coordinates on this line have the same color temperature. Give a picture. The figures in the figure show the "isotherm", the curve is the "blackbody trajectory", and the ellipse is the coordinate range of 6500k lamp stipulated by the state.
The table below for details
Chromaticity coordinate is the coordinates of colors. Now commonly used color coordinates, the horizontal axis is x, and the vertical axis is y. With chromaticity coordinate coordinates, a point can be determined on the chromaticity coordinate. This point accurately represents the luminous color. That is, the chromaticity coordinate accurately represent the color. Because the chromaticity coordinate has two numbers and is not intuitive, people like to use the color temperature to roughly express the luminous color of the lighting source. In fact, the color temperature is calculated through the chromaticity coordinate, and the color temperature cannot be obtained without the chromaticity coordinate. If it has a very dark color, such as green, blue, etc. you can calculate the "main wavelength" and "color purity" through the chromaticity coordinate to visually represent the color. For energy-saving lamps, the state has stipulated the following chromaticity coordinate requirements, and the deviation value is less than 5SDCM.
Number Name Symbol X Y Color temperature Ra
F6500 daylight color RR .313 .337 6430 80
F5000 neutral white RZ .346 .359 5000 80
F4000 cold white RL .380 .380 4040 80
F3500 white RB .409 .394 3450 80
F3000 warm white RN .440 .403 2940 82
F2700 incandescent color RD .463 .420 2720 82
The attached drawings and the energy star standard
Among the three primary colors, only red has a color temperature of about 900K, while other colors have no concept of color temperature. E.g.: iron will not turn green or blue no matter how it is heated. Color temperature is used to represent the color of illumination light (near white). Low color temperature, white with yellow, called warm tone; High color temperature, white with blue, called cold tone. Green light cannot be expressed by color temperature; Blue light also does not has color temperature.
We can see that the difference of chromaticity coordinates at both ends of the isotherm is obvious, that is, the correlated color temperature is the same (i.e. on the isotherm), but the color difference of its light may also be seen by the human eye. When there is a certain difference in the correlated color temperature, color difference is more likely to occur. Generally, LED manufacturers classify their LED correlated color temperature according to the requirements of corresponding standards. There is no problem in the application of general lighting places, but in the application occasions with strict color difference requirements, LED products with fine color coordinates must be selected for production.
The following is the reference given by Energy Star:
Reference of some manufacturers:
(Some pictures come from the Internet. If there is infringement, please contact us and delete them immediately)
Post time: Dec-08-2022